[Southeast University News Network, March 3] (Correspondents: Li Dongmei, Liang Gaolin) On Feb. 26, the internationally renowned academic periodical “Advanced Functional Materials” published the collaborative research results achieved by Professor Liang Gaolin’s team and Professor Wu Fugen’s team from the School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering of Southeast University. With the title of “Enzyme-Mediated Tumor Starvation and Phototherapy Enhance Mild-Temperature Photothermal Therapy”, this paper proposed an enzyme-mediated strategy for tumor starvation and phototherapy, representing a significant progress in enhancing the efficiency of mild-temperature photothermal treatment of tumors (Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 1909391).
Photothermotherapy (PTT) uses the high heat (above 45℃) generated by laser radiation to destroy cancer cells and has gradually become an important approach for cancer treatment. However, the high heat may result in damages of healthy tissue, tumor metastasis and recurrence, etc.; therefore, the use of mild PTT (below 45 ℃) can treat tumor without side effects, but the strategies to maximize the efficiency of mild PTT while avoiding any side effect in solid tumors have not yet been reported.
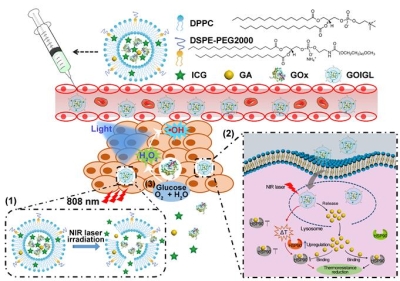
Professor Liang Gaolin's team and Professor Wu Fugen’s team have designed a multifunctional temperature-sensitive liposome in a rational manner, and prepared a temperature-sensitive phase-change liposome through the lipid molecules DPPC and DSPE-PEG2000 to encapsulate glucose oxidase (GOx), indocyanine green (ICG) and gambogic acid (GA). The drug-loaded temperature-sensitive liposomes GOIGLs have realized the thermal response delivery and the mid hypothermia of these drugs at tumor sites (see the figure below).
Both the cell and the animal experiments indicated that this tumor starvation and phototherapy strategy has significantly improved the efficiency of mild PTT in treating tumors; in addition, this strategy has provided a feasible and reliable method to solve the contradiction between mild-temperature photothermal efficiency and dosage. More importantly, this smart strategy by using the enzyme-mediated tumor starvation and phototherapy to enhance the efficiency of mild-temperature photothermal therapy is expected to accelerate the clinical transformation of photothermal therapy.
Schematic diagram of coordinated functions of tumor starvation therapy, enzyme-enhanced phototherapy and hypothermia.
Schematic diagram of multifunctional temperature-sensitive liposomes for synergistic starvation therapy, enzyme-enhanced phototherapy and mild hypothermia in tumor area.
Schematic diagram of multifunctional temperature-sensitive liposomes for synergistic starvation therapy, enzyme-enhanced phototherapy and mild hypothermia in tumor area.
The first author of the paper is Gao Ge, a doctoral student from the School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering of Southeast University. Professor Liang Gaolin and Professor Wu Fugen are co-corresponding authors.
This project has gained fund from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and National Key Research & Development Program.
The paper link: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201909391
Submitted by: the School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering
(Editor-in-charge: Zhai Mengjie, reviewed by: Li Xiaonan)
















