Recently, the research group leading by Prof. Liu Songqin and the research group leading by Prof. Zhang Yuanjian from Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Department of Southeast University and Jiangsu Engineering Laboratory of Smart Carbon-Rich Materials and Device made significant progress in the field of new nano-interface construction and functionalization respectively. The research results were published in international top journal “Journal of the American Chemical Society” (JACS).
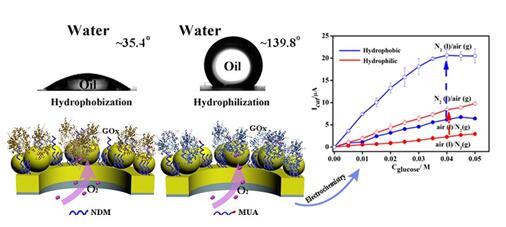
The low solubility of gases in aqueous solution is the major kinetic limitation of reactions that involve gases. To address this challenge, Prof. Liu Songqin’s group reports a nanochannel reactor with joint gas–solid–liquid interfaces and controlled wettability. As a proof of concept, a porous anodic alumina (PAA) nanochannel membrane with different wettability is used for glucose oxidase (GOx) immobilization, which contacts with glucose aqueous solution on one side, while the other side gets in touch with the gas phase directly. Interestingly, it is observed that the O2 could participate in the enzymatic reaction directly from gas phase through the proposed nanochannels, and a hydrophobic interface is more favorable for the enzymatic reaction due to the rearrangement of GOx structure as well as the high gas adhesion. As a result, the catalytic efficiency of GOx in the proposed interface is increased up to 80-fold compared with that of the free state in traditional aqueous air-saturated electrolyte. This triphase interface with controlled wettability can be generally applied to immobilize enzymes or catalysts with gas substrates for high efficiency. The research results were published in “Journal of the American Chemical Society”. The first author is doctoral candidate Mi Li, and the corresponding authors are Prof. Liu Songqin and Prof. Tian Ye from Institute of Chemistry of Chinese Academy of Science.
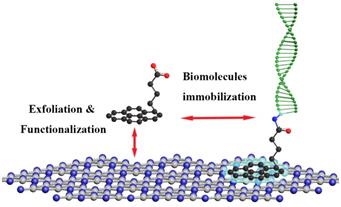
Moreover, the research group leading by Prof. Zhang Yuanjian made important progress in 2Dcarbon nitride(CN) exfoliation and noncovalent interfacial functionalization.
As an emerging nitrogen-rich 2D carbon material, graphitic carbon nitride (CN) has drawn much attention for applications ranging from photo-/electrocatalysts to biosensors. Interfacial modification of CN is fundamentally vital but is still in its infancy and remains challenging due to the low reactivity of CN. The research reports that, in conjunction with a π-π stacking interaction, bulk CN could be simultaneously exfoliated via facile mechanical grinding. The obtained CN nanosheets (m-CNNS) not only retained the pristine optoelectronic properties of bulk CN but also enriched a friendly interface for further coupling biomolecules with advanced properties, overcoming the deficiencies of CN in surface science. The m-CNNS were further covalently linked to a DNA probe, and the resultant electrochemiluminescent biosensor for the target DNA exhibited much enhanced sensitivity with respect to that obtained by direct physical absorption of the DNA probe on unmodified CNNS. This noncovalent exfoliation and interfacial modification should greatly expand the scope of potential applications of CN in areas such as biosensing and should also be applicable to other 2D materials in interface modulation. Besides, in another work of the research group, interfacial functionalized carbon nitride (CN) nanofibers were synthesized by hydrolyzing bulk CN in sodium hydroxide solution. The reversible assemble and disassemble behavior of the as-prepared CN nanofibers was investigated by using CO2 as a trigger to form a hydrogel network at first. Compared to the most widespread absorbent materials such as active carbon, graphene and previously reported supramolecular gel, the proposed CN hydrogel not only exhibited a competitive absorbing capacity (maximum absorbing capacity of methylene blue up to 402 mg/g) but also overcame the typical deficiencies such as poor selectivity and high energy-consuming regeneration. This work would provide a strategy to construct a 3D CN network and open an avenue for developing smart assembly for potential applications ranging from environment to selective extraction. The research results were published in Journal of the American Chemical Society and ACS Nano respectively. The first authors are doctoral candidate Ji Jingjing and Zhang Yuye. The corresponding author is Prof. Zhang Yuanjian.
The above researches were supported by National Research Foundation, Young Overseas High-level Talents Introduction Plan of the Organization Department of the Central Committee of the CPC, and Science and Technology Department of Jiangsu Province, etc..
















